CCNA 200-301 Chapter 2 Network Access Lab 025 Configure Wireless LAN AP via the GUI
Watch Full Demo on YouTube:
Lab Objective:
The primary objective of this lab is to understand the basics of WLAN configuration and management. By the end of this lab, you will be able to configure an Access Point (AP) using the GUI in Cisco Packet Tracer. You will learn how to set up an SSID for your WLAN, configure appropriate security settings to protect your network, and assign IP addresses to wireless clients through DHCP.
Another critical objective is to verify connectivity and security within the network. You will ensure that the wireless clients can communicate with each other and with the router, and that the security settings effectively protect the WLAN from unauthorized access. This hands-on experience will reinforce your understanding of wireless network configuration and management, preparing you for real-world networking scenarios.
Lab Topology:
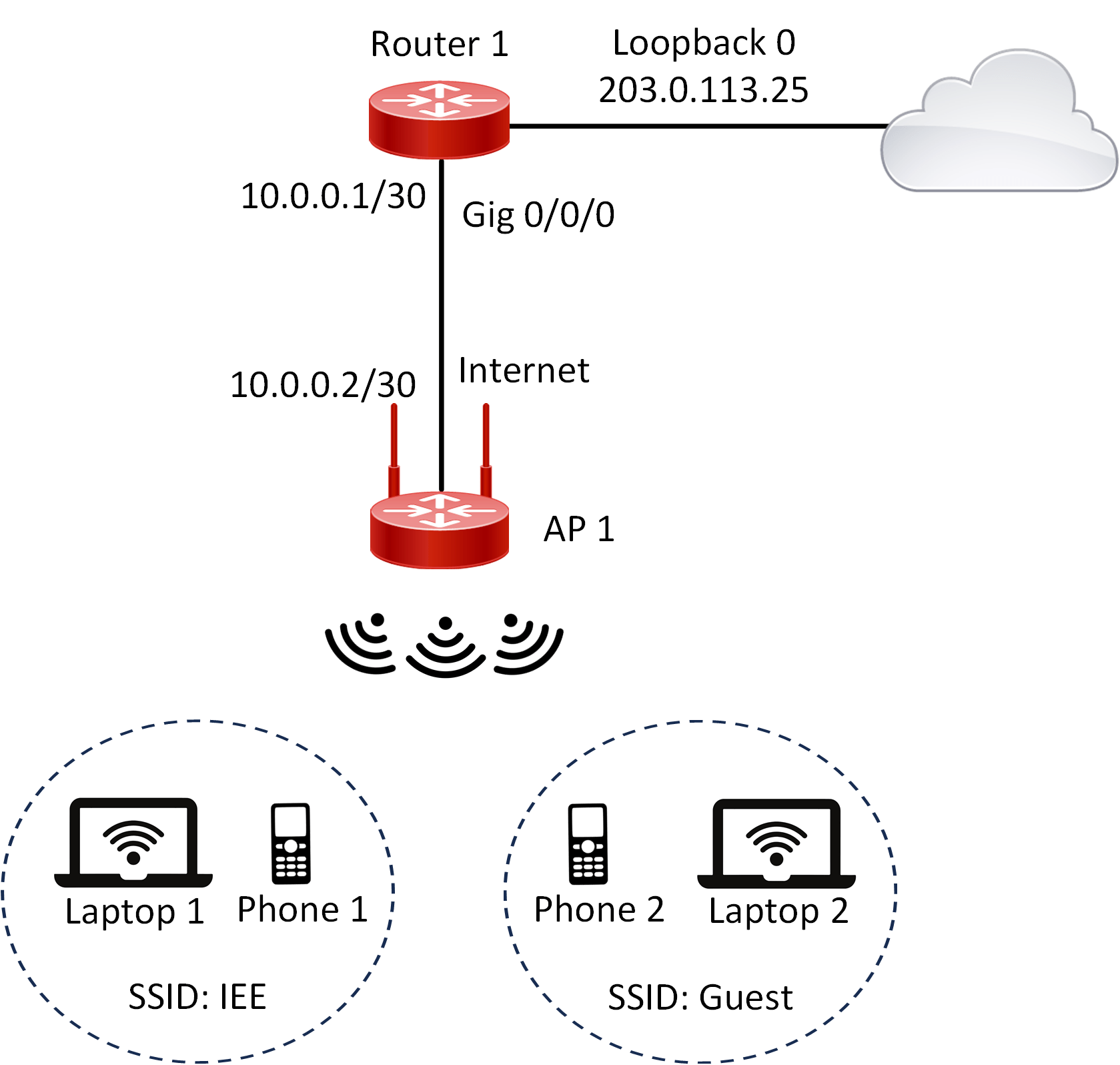
Equipment Required:
- 1x Cisco Router (e.g., Cisco ISR4331/K9)
- 1 x Cisco Wireless Router (e.g., Home-Router-PT-AC)
- 2 x laptops with Wireless interface
- 2 x Smart Phones
- Console Cable
- Ethernet Cable for connections between devices
- Computer with Terminal emulation software e.g. PuTTY
IPv4 Address Table:
A. IPv4 Address Table:
| Device Name | Interface ID | IP Address | Subnet-Mask |
| Router 1 | Gig0/0/0 | 10.0.0.1 | 255.255.255.252 |
| Router 1 | Loopback0 | 203.0.113.25 | 255.255.255.255 |
| AP 1 | Internet | 10.0.0.2 | 255.255.255.252 |
B. Hosts IP Address Table:
| Device Name | Interface ID | IPv4 Address/Subnet-Mask/Default Gateway | SSID | Frequency Band |
| Laptop 1 | Wireless 0 | DHCP | IEE | 2.4 GHz |
| Phone 1 | Wireless 0 | DHCP | IEE | 2.4 GHz |
| Laptop 2 | Wireless 0 | DHCP | Guest | 2.4 GHz |
| Phone 2 | Wireless 0 | DHCP | Guest | 2.4 GHz |
List of Command Summary:
| Command | Command Description |
| enable | enters privileged EXEC mode. |
| configure terminal | enters global configuration mode from privileged EXEC mode. |
| hostname [hostname] | assign a device name to router. |
| show interfaces status | provides a summary of the current status of all interfaces on a Cisco switch. This command displays important information about each interface, including: Port: The interface identifier (e.g., Gi1/0/1). Name: The name or description assigned to the interface, if any. Status: The operational status of the interface (e.g., connected, notconnect, err-disabled). Vlan: The VLAN that the interface is assigned to. Duplex: The duplex mode of the interface (e.g., full, half, auto). Speed: The speed of the interface (e.g., 10, 100, 1000 Mbps, auto). Type: The type of interface (e.g., 10/100/1000BaseTX, SFP). This command is useful for quickly assessing the operational state and configuration details of all interfaces on the switch. |
| ip address [IPv4] [Subnetmask] | used to assign a specific IPv4 address and subnet mask to a network interface on a device such as a router or Layer 3 switch. This configuration allows the interface to participate in the specified IP network, enabling it to communicate with other devices in that network and perform routing functions. |
| description “DESCRIPTION OF SOME SORT” | used to assign a descriptive text label to a network interface on a device such as a router or switch. This description helps administrators to identify the purpose or details of the interface more easily when managing and troubleshooting the network. |
| show ip interface brief | include lan | used on Cisco devices to display a summarized list of all IP interfaces configured on the device and filter the output to only show interfaces that contain the keyword “lan” in their configuration. This command is helpful for quickly identifying and troubleshooting interfaces related to LAN (Local Area Network) configurations within the device’s network environment |
| ipconfig /all | used in Windows operating systems to display detailed information about all network interfaces and their configurations. |
| no shutdown | enables an interface. |
| show running-config | save the running configuration to the startup-configuration file. |
| show running-config | section interface GigabitEthernet0/* | used to display the configuration details of a specific GigabitEthernet interface (interface GigabitEthernet0/) within the running configuration of a Cisco device. This command allows you to view the configuration settings related to the specified interface only, filtering out other configuration sections. It provides a focused view of the configuration parameters associated with the specified interface, including its IP address, VLAN membership, trunking settings, and any other relevant configuration details. The asterisk (*) is a wildcard character that matches any character or sequence of characters. In this context, it is used to match any subinterface under GigabitEthernet0. |
| show running-config | section interface FastEthernet0/1$ | The “show running-config | section interface FastEthernet0/1$” command is similar to the previous one, but it focuses specifically on the FastEthernet0/1 interface. The “$” symbol at the end of the interface name indicates that the command will match only the interface that ends with “FastEthernet0/1”. This command is helpful when you want to view the configuration details of a specific FastEthernet interface without displaying configurations for other interfaces. |
| copy running-config startup-config | used to save the currently running configuration (stored in the RAM) to the startup configuration (stored in the NVRAM) |
| end | exit configuration mode. |
| exit | exits one level in the menu structure command. |
Lab Task:
- Router1 Configuration:
- Configure interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0 with the following attributes:
- Configure an appropriate interface description.
- Configure IPv4 address with Subnet-Mask, refer to the lab table.
- Enable the interface.
- Create a local account “IEE” with a secret password of “IEE” with the highest privilege level and create a secret password for EXEC Mode, use this password “IEE”.
- Use the appropriate commands to enable Telnet on the router.
- Configure interface loopback 0 with this IPv4 address 203.0.113.25/32 to mimic a server from the internet
- Perform post check to verify your configuration.
- Configure interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0 with the following attributes:
- AP1 Configuration via the GUI interface:
- Configure Internet Interface with the appropriate IPv4 address information, in addition, please use 8.8.8.8 in the DNS1 entry. You must perform this step manually.
- Configure the LAN network with the following IPv4 address details:
- Enable DHCP
- Use this IPv4 address range 172.16.0.0/24
- Start IP Address from 172.16.0.100
- Set the maximum number of Users to 150
- Set the first DNS entry with 8.8.8.8
- Create an SSID “IEE” for the 2.4 GHz frequency band:
- Network Mode: Auto
- Network Name SSID: IEE
- SSID Broadcast: Enable
- Standard Channel: Default
- Channel Bandwidth: Auto
- Disable 5 GHz-1 and 5 GHz2 frequency band
- Set the following attribute under the Wireless Security setting:
- Security Mode: WPA2 Personal
- Encryption Type: AES
- Passphrase: “IEE123456”
- Disable both frequency 5GHz-1 and 5GHz-2
- Set the following under the Guest Network:
- Enable Guest Profile for the 2.4 GHz frequency
- Set the following attributes:
- Network Name (SSID): Guest
- Enable Broadcast SSID
- Security Mode: WPA2 Personal
- Encryption Type: AES
- Passphrase: Guest123456
- Disable Guests to see each other and access the local network
- Disable 5 GHz-1 and 5 GHz-2 Guest Profiles
- End host configuration:
- Configure Laptop 1 and Phone 1 with the following Wireless attributes:
- SSID: IEE
- Authentication: WPA2-PSK
- PSK Pass Phrase: IEE123456
- Encryption Type: AES
- Configure Laptop 2 and Phone 2 with the following Wireless attributes:
- SSID: Guest
- Authentication: WPA2-PSK
- PSK Pass Phrase: Guest123456
- Encryption Type: AES
- Set the Wireless0 interface on each end host to use DHCP
- Verify that each end host has an appropriate IP address
- Configure Laptop 1 and Phone 1 with the following Wireless attributes:
- Connectivity Test:
- Initiate a ping from each end host in the IEE network to the default gateway
- Initiate a ping from each end host to 203.0.113.25
- Initiate a ping from Laptop 1 to Phone 1.
- Initiate a ping from Laptop 2 to Laptop 1, is the ping successful?
- Initiate a telnet session from Laptop 1 to Router 1. You should be able to login to the router using local account creds. If you are unable then troubleshoot the problem.
- Initiate a HTTP Session from Laptop 1 to AP 1 on 10.0.0.2
- Configure Access Policies on AP 1:
- Create a new policy “block_telnet”
- Enable the policy
- Edit the list to apply it to Phone 1
- Add Telnet (22-23) and HTTP/HTTPS under the Blocked List section
- Save the configuration
- Initiate a telnet test from Phone 1 to Router 1. Was this successful?
- Initiate a HTTP session to 10.0.0.2 from Phone 1. Was this successful?
- Initiate a telnet and HTTP session from Laptop 1, please use 10.0.0.1 for Telnet and 10.0.0.2 for HTTP protocols.
- Configure QoS settings on AP 1:
- Retrieve Laptop 1 MAC address
- Create a new entry under QoS section and set the MAC address
- Set the priority to High
- Save the configuration
Lab Solution:
1- Router1 Configuration:
a. Configure interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0 with the following attributes:
1) Configure an appropriate interface description.
2) Configure IPv4 address with Subnet-Mask, refer to the lab table.
3) Enable the interface.
On Router1:
Router1#configure terminal
Router1(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 0/0/0
Router1(config-if)#description “Link to AP 1”
Router1(config-if)#ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.252
Router1(config-if)#no shut
Router1(config-if)#
b. Create a local account “IEE” with a secret password of “IEE” with the highest privilege level and create a secret password for EXEC Mode, use this password “IEE”.
On Router1:
Router1(config)#username IEE privilege 15 secret IEE
c. Use the appropriate commands to enable Telnet on the router.
Router1(config)#lin
Router1(config)#line vty
Router1(config)#line vty 0 4
Router1(config-line)#logging synchronous
Router1(config-line)#login local
Router1(config-line)#transport input telnet
Router1(config-line)#end
Router1#
d. Configure interface loopback 0 with this IPv4 address 203.0.113.25/32 to mimic a server from the internet
Router1#configure terminal
Router1(config)#interface loopback 0
Router1(config-if)#ip address 203.0.113.25 255.255.255.255
Router1(config-if)#end
Router1#
e. Perform post check to verify your configuration.
Perform in-flight checks:



2- AP1 Configuration via the GUI interface:
a. Configure Internet Interface with the appropriate IPv4 address information, in addition, please use 8.8.8.8 in the DNS1 entry. You must perform this step manually.
Select GUI -> Setup -> Internet Setup -> Connection Type -> Static IP

Save the settings
b. Configure the LAN network with the following IPv4 address details:
1) Enable DHCP
2) Use this IPv4 address range 172.16.0.0/24
3) Start IP Address from 172.16.0.100
4) Set the maximum number of Users to 150
5) Set the first DNS entry with 8.8.8.8
Select GUI -> Setup -> Internet Setup -> Network Setup -> Router IP

c. Create an SSID “IEE” for the 2.4 GHz frequency band:
1) Network Mode: Auto
2) Network Name SSID: IEE
3) SSID Broadcast: Enable
4) Standard Channel: Default
5) Channel Bandwidth: Auto
d. Disable 5 GHz-1 and 5 GHz2 frequency band
Select GUI -> Wireless -> Basic Wireless Settings

e. Set the following attribute under the Wireless Security setting:
1) Security Mode: WPA2 Personal
2) Encryption Type: AES
3) Passphrase: “IEE123456”
4) Disable both frequency 5GHz-1 and 5GHz-2
Select GUI -> Wireless -> Wireless Security

f. Set the following under the Guest Network:
1) Enable Guest Profile for the 2.4 GHz frequency
2) Set the following attributes:
1- Network Name (SSID): Guest
2- Enable Broadcast SSID
3- Security Mode: WPA2 Personal
4- Encryption Type: AES
5- Passphrase: Guest123456
3) Disable Guests to see each other and access the local network
4) Disable 5 GHz-1 and 5 GHz-2 Guest Profiles
Select GUI -> Wireless -> Guest Network

- End host configuration:
a. Configure Laptop 1 and Phone 1 with the following Wireless attributes:
1) SSID: IEE
2) Authentication: WPA2-PSK
3) PSK Pass Phrase: IEE123456
4) Encryption Type: AES
On Laptop 1:

On Phone 1:

b. Configure Laptop 2 and Phone 2 with the following Wireless attributes:
1) SSID: Guest
2) Authentication: WPA2-PSK
3) PSK Pass Phrase: Guest123456
4) Encryption Type: AES
On Laptop 2:


c. Set the Wireless0 interface on each end host to use DHCP
Select Desktop -> IP Configuration -> Interface Wireless 0 -> DHCP

d. Verify that each end host has an appropriate IP address
You can see from the image above that each end host manage to obtain an IPv4 address information. Also, you can do this via issuing this command from the CLI of the end host “ipconfig /all”:

4- Connectivity Test:
a. Initiate a ping from each end host in the IEE network to the default gateway


b. Initiate a ping from each end host to 203.0.113.25

c. Initiate a ping from Laptop 1 to Phone 1.

d. Initiate a ping from Laptop 2 to Laptop 1, is the ping successful?

e. Initiate a telnet session from Laptop 1 to Router 1. You should be able to login to the router using local account creds. If you are unable then troubleshoot the problem.
Select Desktop -> Telnet/SSH Client -> Connection Type -> Telnet
On Laptop 1:


On Phone 1:

f. Initiate a HTTP Session from Laptop 1 to AP 1 on 10.0.0.2

The password is admin/IEE

5- Configure Access Policies on AP 1:
a. Create a new policy “block_telnet”
b. Enable the policy
Select GUI -> Access Restrictions -> Internet Access Policy ->
Enter Policy Name

c. Edit the list to apply it to Phone 1
Select Edit List from Applied PCs Option and add Phone 1’s IP address and save the setting before you hit the Close button:

Add Telnet (22-23) and HTTP/HTTPS under the Blocked List section

e. Save the configuration
6- Initiate a telnet test from Phone 1 to Router 1. Was this successful?
No the session didn’t establish due to the policy being applied on AP 1.

7- Initiate a HTTP session to 10.0.0.2 from Phone 1. Was this successful?
Again, no because of the ACL applied on AP 1

8- Initiate a telnet and HTTP session from Laptop 1, please use 10.0.0.1 for Telnet and 10.0.0.2 for HTTP protocols.
Yes connection was successful as expected


9- Configure QoS settings on AP 1:
a. Retrieve Laptop 1 MAC address

b. Create a new entry under QoS section and set the MAC address
c. Set the priority to High
Select GUI -> Applications and Gaming -> QoS -> Enable

10- Save the configuration
Conclusion:
In this lab, we successfully configured a Wireless LAN using the GUI in Cisco Packet Tracer. By setting up an SSID, configuring security settings, and ensuring proper IP addressing, we provided secure and efficient wireless access for our network clients. This lab highlights the importance of securing wireless networks and the practical steps involved in configuring and managing WLANs.
Packet Tracer Lab (Pre/Post configuration):
Download the file below and open the word document to access the Packet Tracer labs.